TiLobeMAXX
Science Meets Unique Solutions
Supported by extensive research, the Molaris Implant Systems TILOBEMAXX® and I-HEXMRT™ pioneered “molar wide” 7, 8 and 9 mm diameter implants, designed for immediate placement in a molar extraction socket. The larger-than-conventional tapered implant body fits the natural shape as the implant engages with the bony perimeter walls achieving primary stability. The wider restorative platform allows for an emergence profile suitable for a molar restoration. Molaris implants with an enhanced surface and an adequate prosthetic platform help to minimize bone loss, support soft tissue and reduce treatment time.
Implant Overview
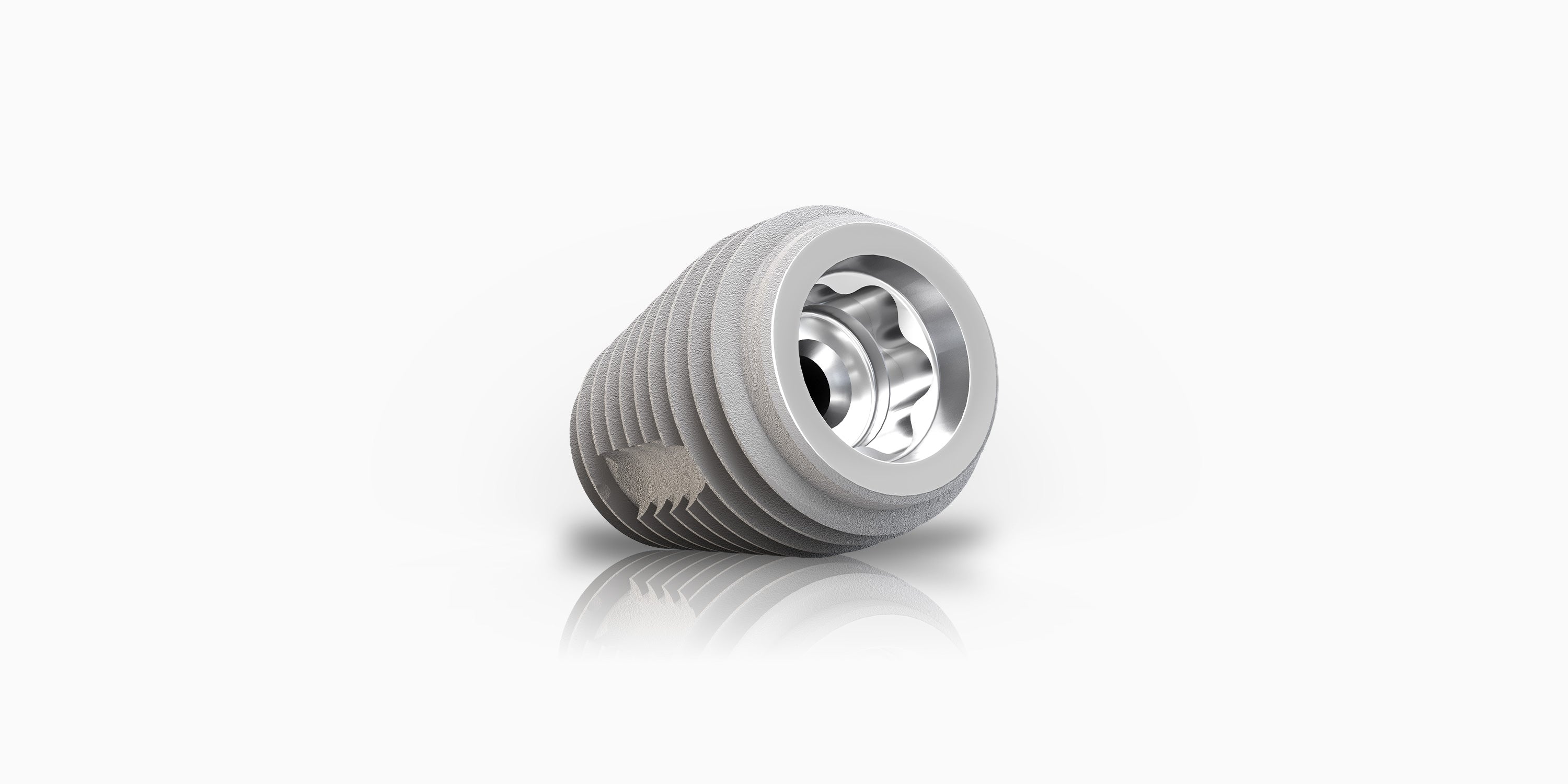
TiLobeMAXX
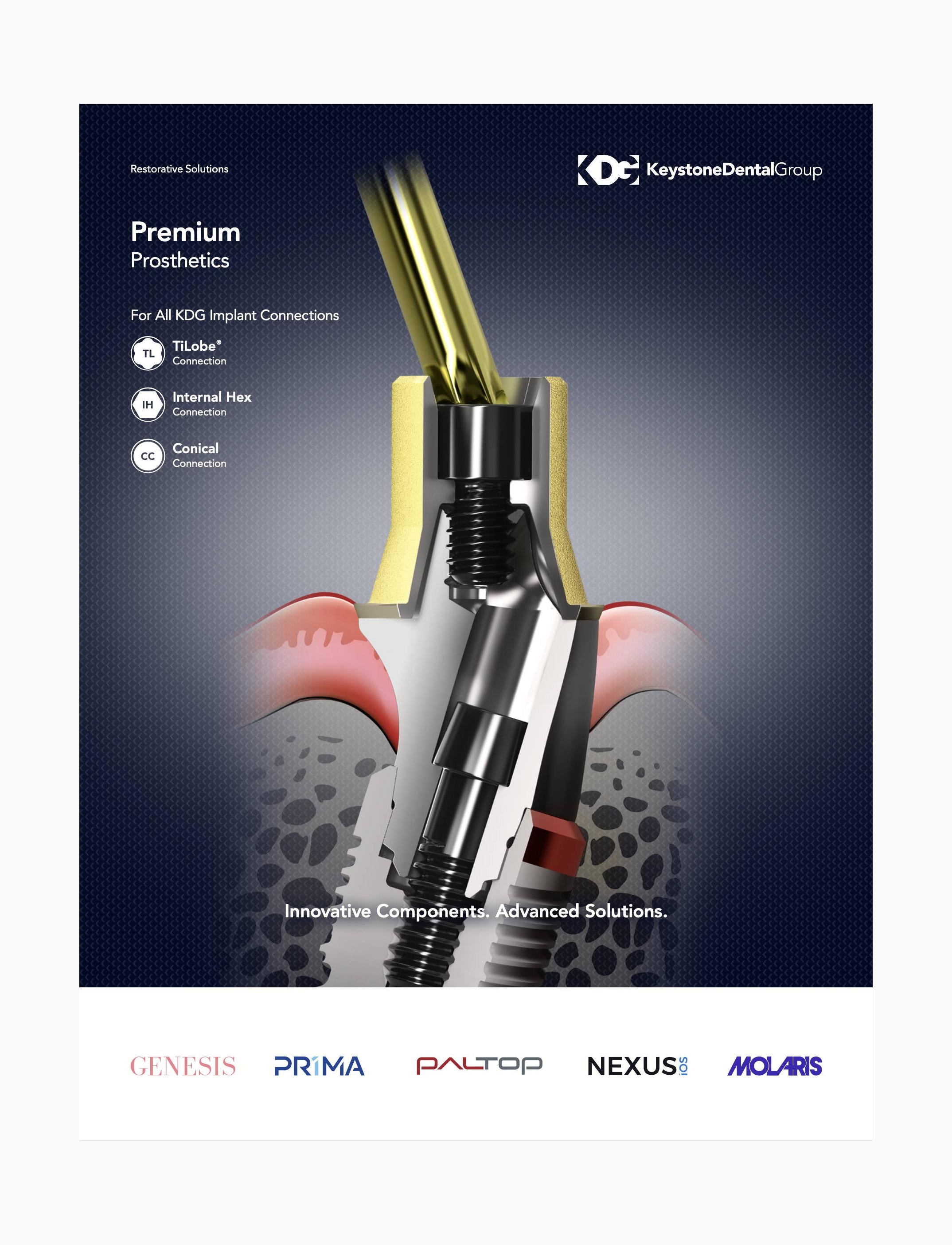
TiLobe® Connection
A versatile TiLobe® six-lobed, color-coded internal connection provides a stable implant and abutment connection.
Platform Switching
The platform switch helps to maintain crestal bone and increase soft tissue volume around the implant platform.
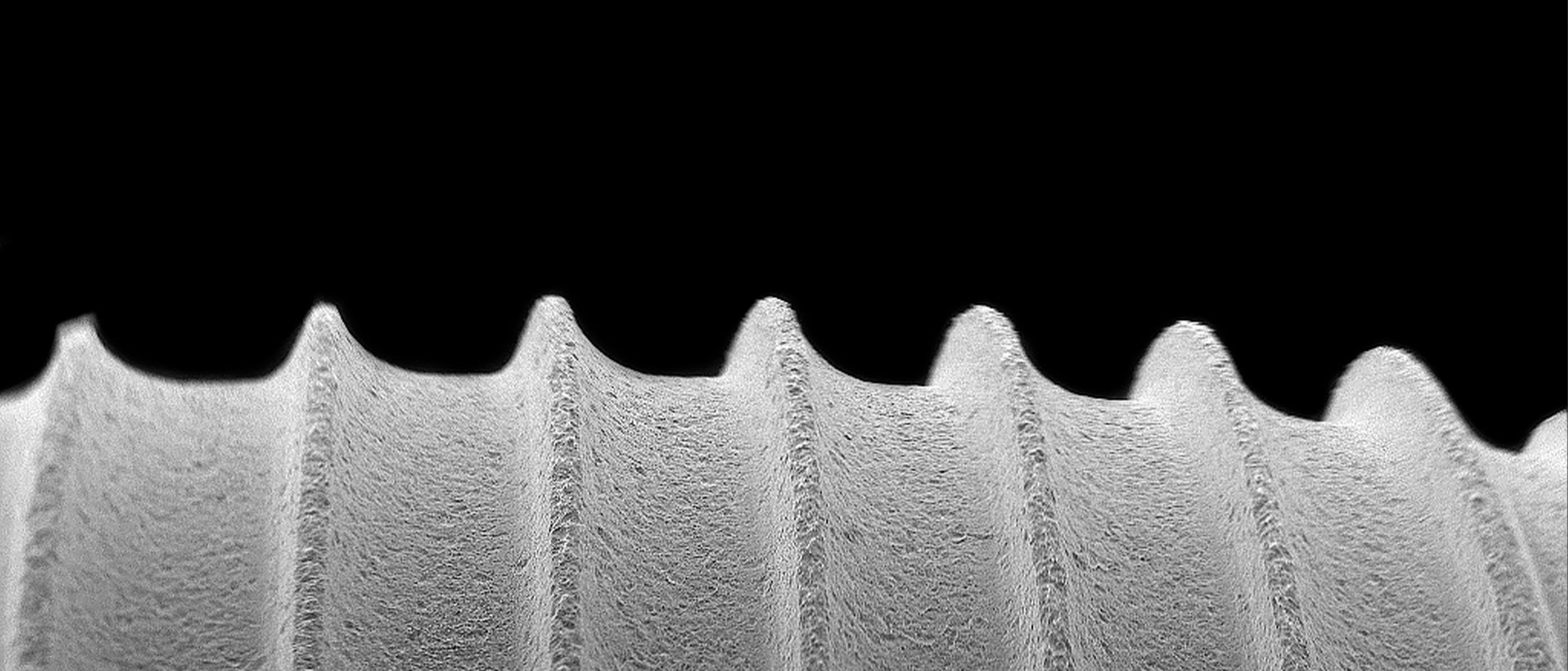
Expanding Shape
The wide body of the implant increases bone-to-implant contact for high primary stability in the molar extraction site.
Rounded Apex
The rounded apex protects the sinus floor and/or adjacent anatomical structures during implant insertion.
Tapered Implant
Fully tapered implant body, with single-lead thread, allows for gradual bone condensing and engagement of the inter-radicular bone for high primary stability within the molar extraction site.
Resource Documents
Molaris Surgical Drill Sequence
References
Scientific Articles
1. AI-Nsour MM, Hsun-Liang C, Wang HL.Effect of the Platform-Switching Technique on Preservation of Peri-implant Marginal Bone: A Systematic Review. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants Volume 27, Number 1, 2012.
2. Cappiello M, Luongo R, Di Iorio D, Bugea C, Cocchetto R, Celletti R. Evaluation of peri-implant bone loss around platform-switched implants. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2008 Aug;28(4):347-55.
3. Prosper L, Redaelli S, Pasi M, Zarone F, Radaelli G, Gherlone EF. A randomized prospective multicenter trial evaluating the platform-switching technique for the prevention of post-restorative crestal bone loss. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009 Mar-Apr;24(2):299-308.
4. Klein M, Tarnow D, Lehrfield L. Marginal Bone Changes on Ultraclean, Micro-Threaded Platform-Switched Implants Following Restoration: 1- to 4-Year Data.
5. Compendium of Continuin Education in Dentistry. Article Vol. 41 No. 4. 2020. Singh Dhaliwal J, Rani Nakka David S, Ramizah Zulhilmi N, Kaur Sodhi Dhaliwal S, Knights J, Ferreira de Albuquerque Junior R. Contamination of titanium dental implants: a narrative review. SN Applied Sciences volume 2, Article number: 1011. 2020.
6. Dr. Dirk Duddeck, Dr. Hassan Maghaireh, Dr. Franz-Josef Faber and Dr. Jorg Neugebauser. SEM surface analyses of 120 sterile-packed implants. EDI Journal. 2014; 64-75.
7. Vandeweghe S, Ackermann A, Bronner J, Hattingh A, Tschakaloff A, De Bruyn H. A Retrospective, Multicenter Study on a Novo Wide-Body Implant for Posterior Regions. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research. 2009, 1-12. Doi 10.1111/j.1708-8208.2009.00253.x.
8. Vandeweghe S, Hattingh A, Wennerberg A, De Bruyn H. Surgical Protocol and Short-Term Clinical Outcome of Immediate Placement in Molar Extraction Sockets Using a Wide Body Implant. J Oral Maxillofac Res 2011 (Jul-Sep);2(3):e1.
9. Vandeweghe S, De Ferrerre R, Tschakaloff A. De Bruyn H. A Wide-Body Implant as an Alternative for Sinus Lift or Bone Grafting. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surgery. 2011;69:e67-e74.
10. Vandeweghe S, Ackermann A, Bronner J, Hattingh A, Tschakaloff A, De Bruyn H. A Retrospective, Multicenter Study on a Novo Wide-Body Implant for Posterior Regions.
11. Atieh A.A./Payne A.G.T., Duncan W.J., DeSilva R.K., Cullinan M.P. Immediate Placement or Immediate Restoration/Loading of Single Implants for Molar Tooth Replacement: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2010; Issue 1, Vol. 25, p. 401-415.
12. Vandeweghe S, Deferrerre R, Tschakaloff A, De Bruyn H. Wide-Body Implant as an Alternative for Sinus Lift or Bone Grafting. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2011; June, Issue 69, Vol. 6, p. e67-74 (Epub 2011 Mar 21).
13. Vandeweghe S, Hattingh A, Wennerberg A, De Bruyn H. Surgical protocol and clinical outcome of immediate placement in molar extraction sockets using a wide body implant. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009; Issue 1 Vol. 24, p. 186-217.
14. Smith R, Tarnow D Classification of Molar Extraction Sites for Immediate Dental Implant Placement: Technical Note. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013; Issue 3, Vol. 28, p. 911-916.
15. Smith R, Rawdin S B., Kagan V. Influence of Implant–Tooth Proximity on Incidence of Caries in Teeth Adjacent to Implants in Molar Sites: A Retrospective Radiographic Analysis of 300 Consecutive Implants. Compendium. January 2020; Issue 1, Vol. 41, p. 38-42.
16. Scheid, Rickne C, and Julian B. Woelfel. Woelfel's Dental Anatomy. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Health, 2012; p. 161-163.