Paltop
Science Meets Innovation
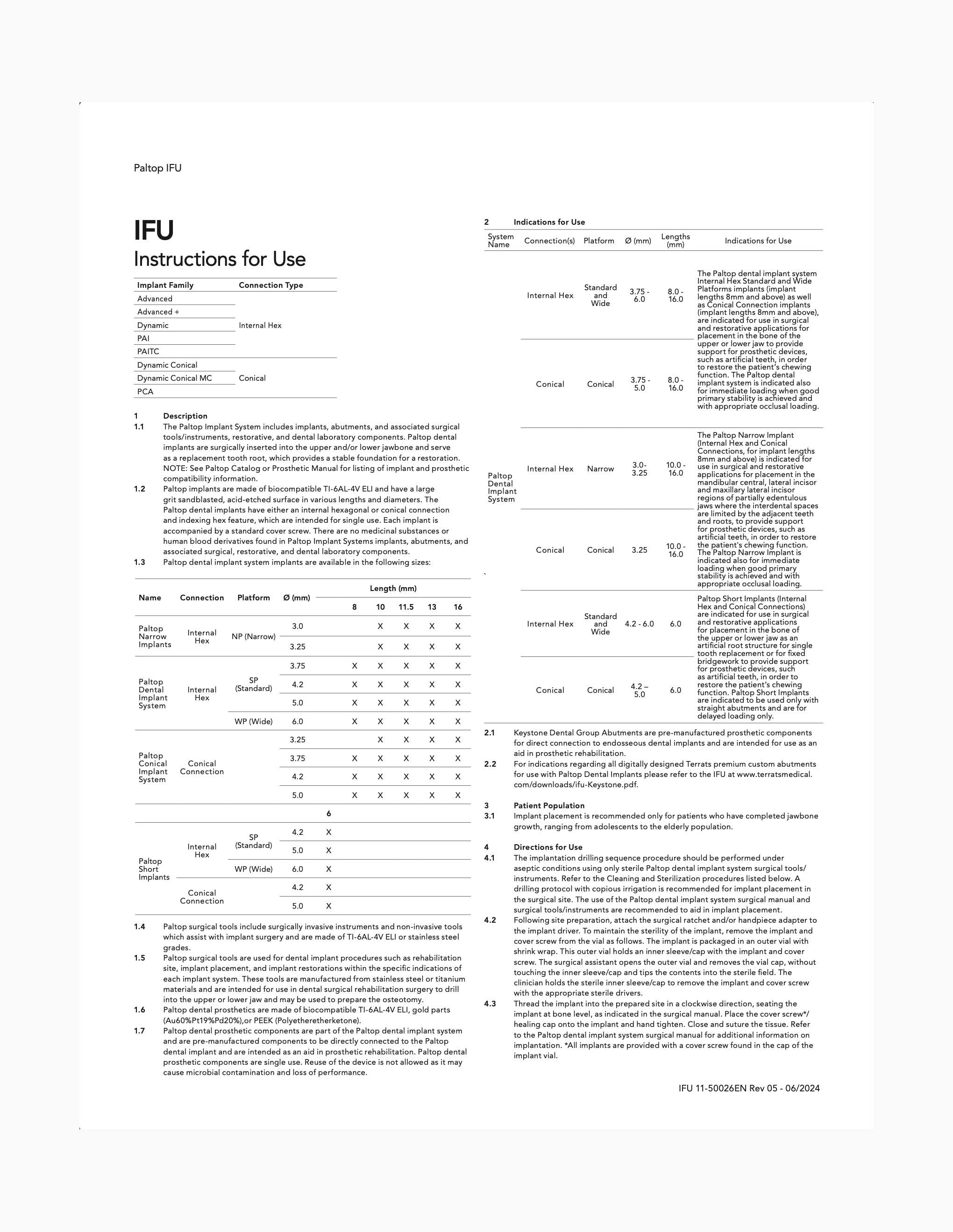
We continue to build on our strong heritage as a contemporary implant system backed by science and innovation. Paltop offers six innovative implants with an advanced biological design, including state-of-the-art surgical and restorative components. This complete implant system with two restorative connections, both engineered for marginal bone preservation and restorative flexibility, can be placed utilizing the Premium Surgical Kit. The hallmark of our restorative components is a unique concave abutment profile, which helps deliver long-term aesthetics. Paltop leads with innovation through unique digital workflows and individual implant solutions, such as the Single-Unit Abutment System (SUA) and the Angulated Corrective System (ACS) designed to deliver excellent treatment outcomes and better patient care.
Implant Overview
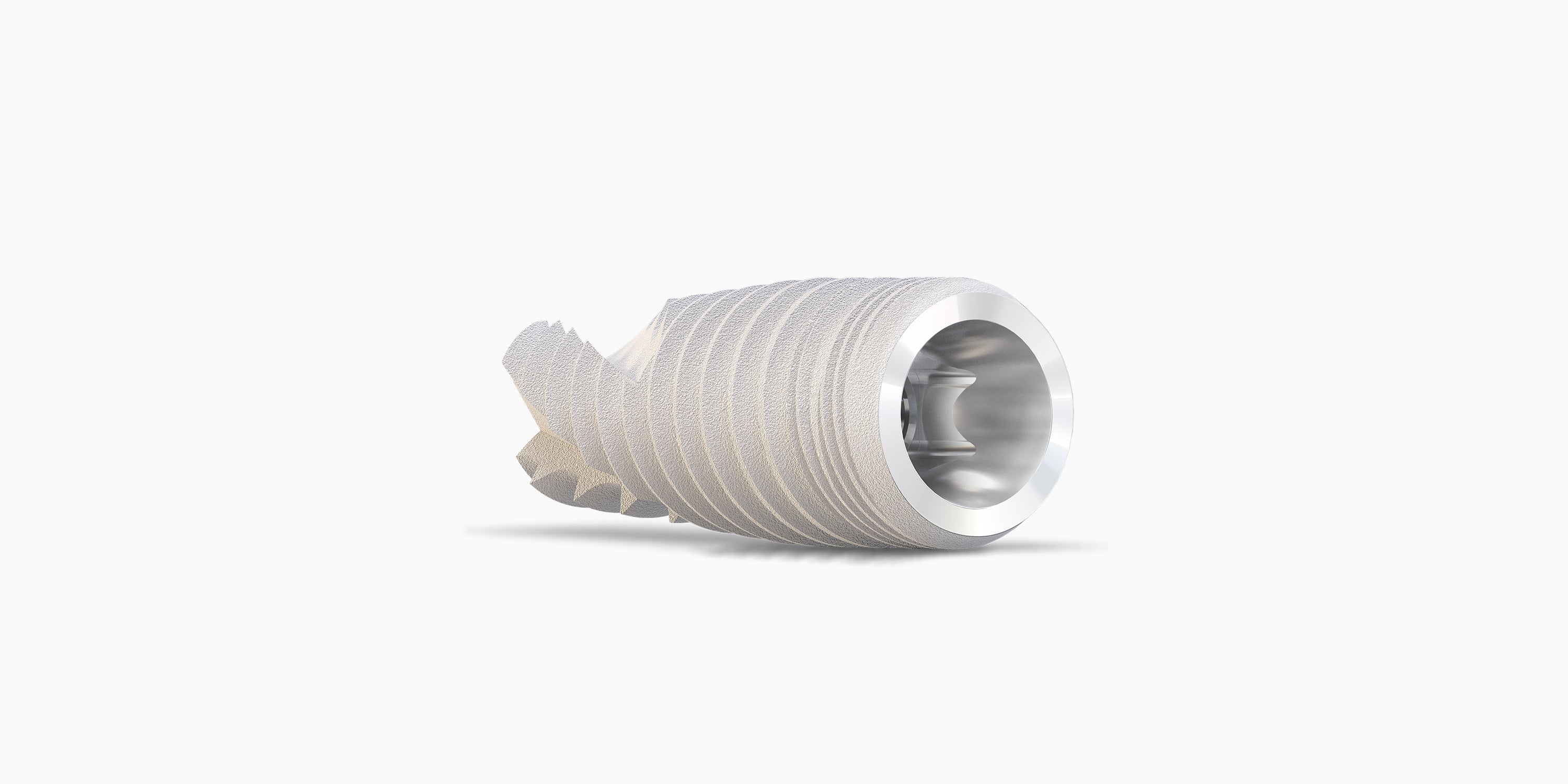
Dynamic Conical
Conical Connection
Tightly sealed conical interface with a deep internal hex connection offers high mechanical strength and platform switching to optimize bone preservation and soft tissue.
Platform Switching
The platform switch maintains crestal bone and increases soft tissue volume around the implant platform.
Bone Maintenance
Microthreads provide even load distribution, stabilizing, and maintaining crestal bone levels.
Thread Design
Double-lead thread with a reverse buttress profile with 0.8 mm thread pitch.
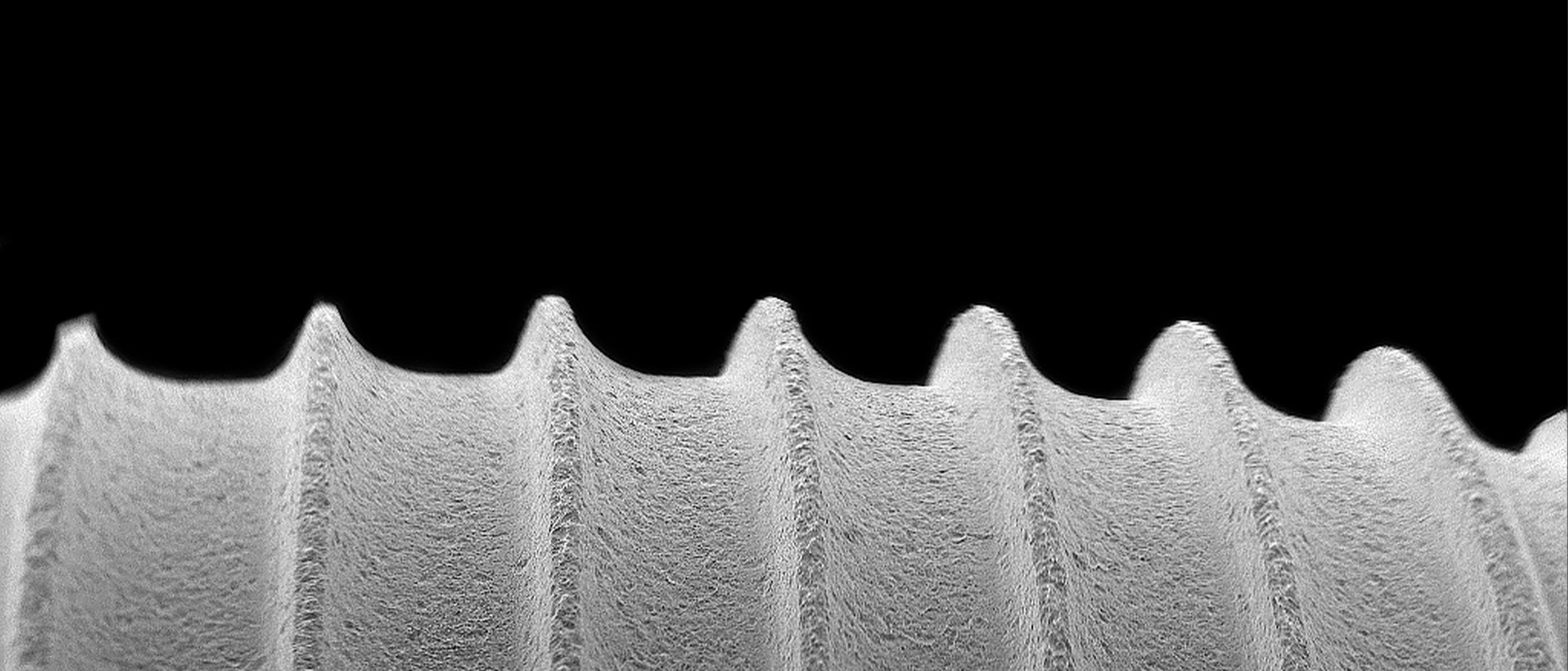
K-LEAN™
Sandblasted acid-etched surface, with an extensive multi-stage cleaning process, utilizes ultra-pure water (UPW) which removes undesired residues, providing a clean surface and maintaining an intact oxide layer.
Cutting Apex
Designed for controlled implant placement in challenging sites.
Tapered Apex
The apically tapered implant design allows for under-preparation of the osteotomy and supports primary stability in soft bone.
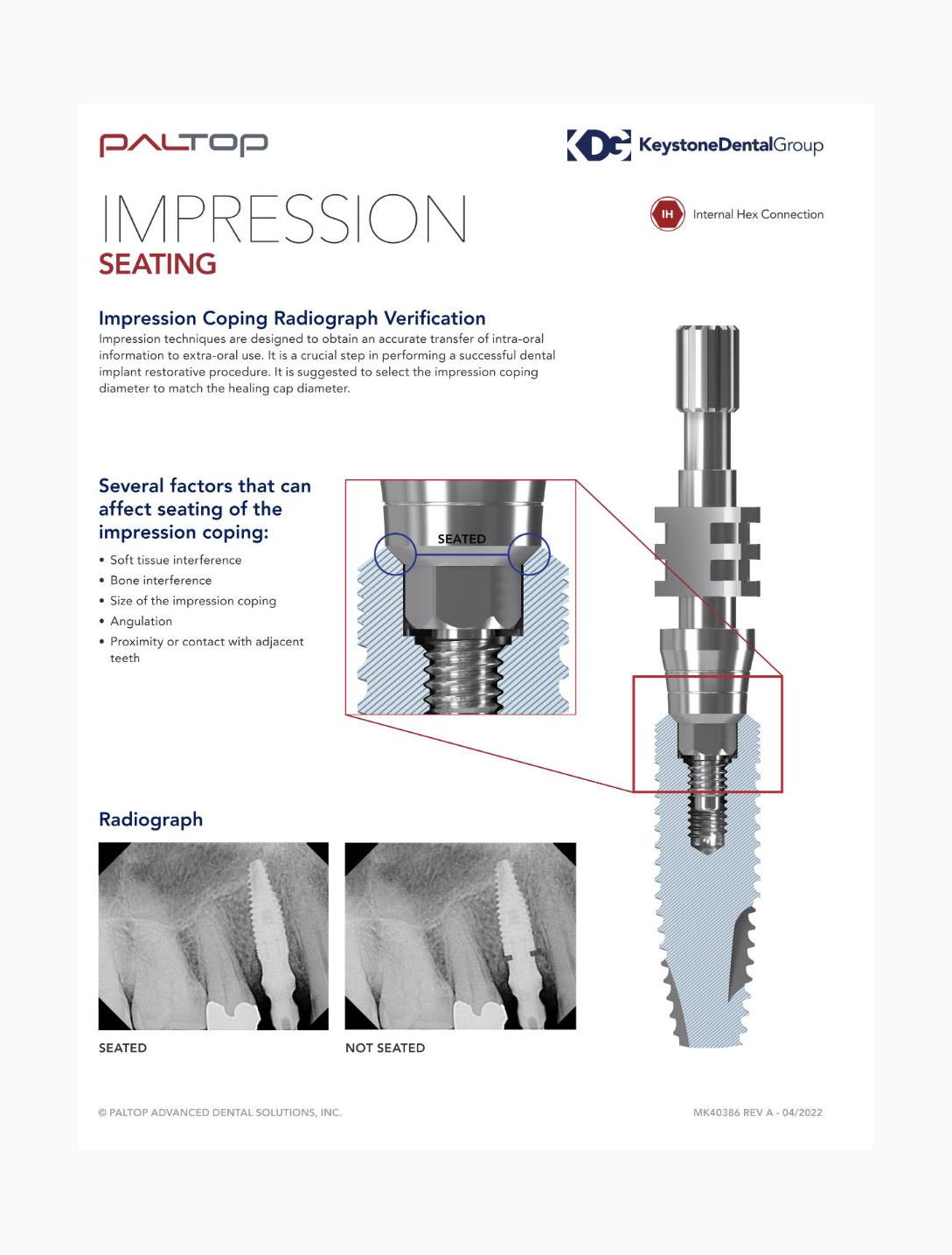
Resource Documents
Paltop Impression Seating Flyer
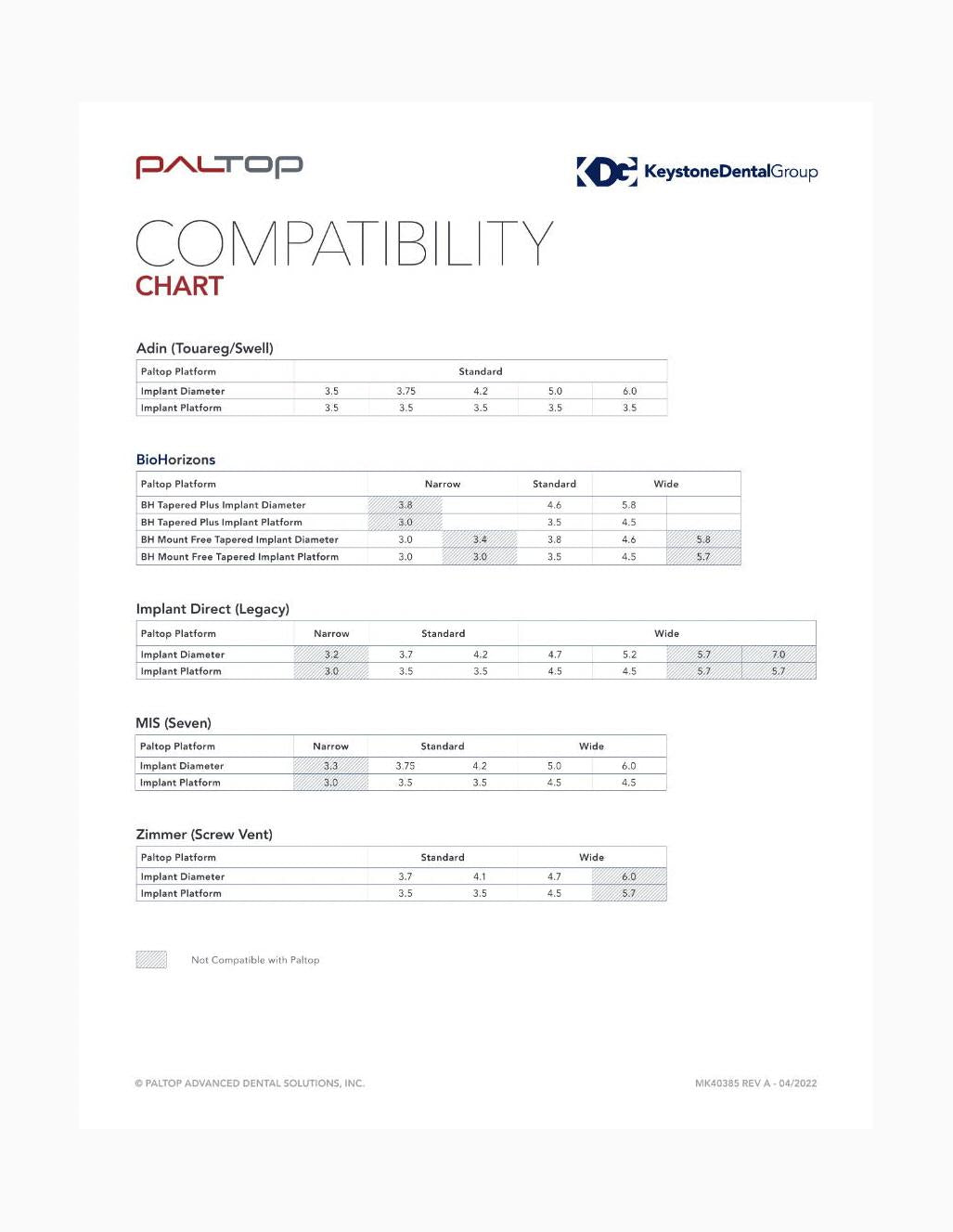
Paltop Implant Compatibility Chart
References
Scientific Articles
1. Redemagni M, Lomazzo C, Cremonesi S, Garlini G, Maiorana C, European Journal of Esthetic Dentistry. Volume 4. Number 4. Winter 2009.
2. López-López P, Mareque-Bueno J, Boquete-Castro A, Aguilar-Salvatierra Raya A, M Martínez-González J, L Calvo-Guirado J. Clin Orla Implants Res. 2016 Jan27(1) :90-6 doi:10.1111/crl.12516. Epub 2014 Oct 31.
3. Rompen E, Raepsaet N, Domken O, Touati B, Van Dooren E. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry. Volume 97. Issue 6 supplement, June 2007, S119-S125.
4. Caram S, Huynh-Ba G, Schoolfield J, Jones A, Cochran D, Belser U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2014;29:1114–1122.
5. Thobity A, Kutkut A, Almas K. J Oral Implantol. 2017 Apr;43(2):157-166. doi: 10.1563/aaid-joi-D-16-00170. Epub 2016 Nov 21.
6. A Bratu E , Tandlich M, Shapira L. A rough surface implant neck with Microthreads reduces the amount of marginal bone loss: a prospective clinical study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009 Aug;20(8):827-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01730.x. Epub 2009 Jun 7.
7. Young-Kyu S , Chong-Hyun H, Seong-Joo H, Sunjai K, Heoung-Jae C. Radiographic evaluation of marginal bone level around implants with different neck designs after 1 year. Int J. Oral Maxillofac Implants. Sep-Oct 2006;21(5):789-94.
8. Klein M, Tarnow D, Lehrfield L. Marginal Bone Changes on Ultraclean, Micro-Threaded Platform-Switched Implants Following Restoration: 1- to 4-Year Data. Compendium of Continuin Education in Dentistry. Article Vol. 41 No. 4. 2020.
9. Singh Dhaliwal J, Rani Nakka David S, Ramizah Zulhilmi N, Kaur Sodhi Dhaliwal S, Knights J, Ferreira de Albuquerque Junior R. Contamination of titanium dental implants: a narrative review. SN Applied Sciences volume 2, Article number: 1011. 2020.
10 .Duddeck D, Maghaireh H, Faber FJ and Neugebauser J. SEM surface analyses of 120 sterile-packed implants. EDI Journal. 2014; 64-75.
11. M. Schmitt C, Nogueira Filho G, C. Tenenbaum H, Yuan Lai J, Brito C, Döring H, Nonhoff J. Performance of conical abutment (morse Taper) connection implants: A Systematic review. J Biomed Mater Res Part A: 102A: 552–574, 2014.
12. Sang-Woon L, Min-Sang C, Ji-Hye L, Lee-Ra C, Chan-Jin P. Joint stability of internal conical connection abutments with or without hexagon indexes: an in vitro study. Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science, 10.14368/jdras.2020.36.2.95, 36, 2, 95-103, 2020.
13. Tsuruta K, Ayukawa Y, Matsuzaki T, Kihara M, Koyano K. The influence of implant-abutment connection on the screw loosening and microleakage. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2018, 4, 1–6.
14. AI-Nsour MM, Hsun-Liang C, Wang HL.Effect of the Platform-Switching Technique on Preservation of Peri-implant Marginal Bone: A Systematic Review. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants Volume 27, Number 1, 2012.
15. Cappiello M, Luongo R, Di Iorio D, Bugea C, Cocchetto R, Celletti R. Evaluation of peri-implant bone loss around platform-switched implants. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2008 Aug;28(4):347-55.
16. Prosper L, Redaelli S, Pasi M, Zarone F, Radaelli G, Gherlone EF. A randomized prospective multicenter trial evaluating the platform-switching technique for the prevention of post-restorative crestal bone loss. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009 Mar-Apr;24(2):299-308.
17. J B Manikyamba Y, Suresh Sajjan MC, Rama Raju A.V., Bheemalingeshwara R. Chandrasekharan Nair K. Implant thread designs: An overview. TPDI. Jan / Jul 2017, Vol. 8, No. 1 & 2.
18. Abuhussein H, Pagni G, Rebaudi A, Wang HL. The effect of thread pattern upon implant osseointegration. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010 Feb;21(2):129-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01800.x. Epub 2009 Aug 25. PMID: 19709058